Tooth pain can be intense, making eating, sleeping, and concentrating on everyday activities difficult. When a tooth infection causes pain, many hope that antibiotics will provide immediate relief. However, antibiotics do not work instantly and may not be the only treatment needed to fully resolve the problem.
If you are wondering, “How soon will antibiotics stop tooth pain?” The answer depends on several factors, including the severity of the infection, the type of antibiotic treatment, and whether you require additional dental work.
This article will explain how antibiotics work when they are needed for a tooth infection, how long they take to relieve dental pain, and why proper dental treatment is often necessary alongside medication.
Why Do Tooth Infections Happen?
A tooth infection develops when bacteria enter the tooth’s pulp, the innermost tissue that contains nerves and blood vessels. This can cause inflammation, severe pain, and swelling. The infection can extend to nearby tissues and bones if left untreated, leading to more severe complications.
Common causes of tooth infections include: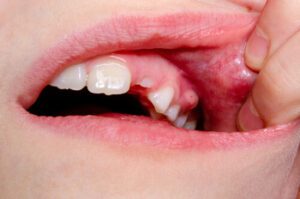
- Tooth decay: If cavities go untreated, bacteria can penetrate deep into the tooth, leading to an infection in the pulp.
- Gum disease: Bacteria from gum infections can spread to nearby bones and tissues, potentially causing a dental infection.
- Tooth abscess: A pocket of pus forms due to an infected pulp, causing intense pain and swelling.
- Dental work: In rare cases, bacteria can enter the tooth during procedures such as a filling, crown, or root canal.
- Weakened immune system: Individuals with conditions like diabetes or autoimmune disorders may have a higher risk of developing serious infections.
When Do You Need Antibiotics for a Tooth Infection?
Not every tooth infection requires antibiotics. In some cases, dental treatment alone is enough to remove the infection. However, a dentist prescribes antibiotics when:
- The infection has extended beyond the affected tooth, reaching the gums, jaw, or facial tissues.
- The patient experiences significant swelling in the face, jaw, or neck.
- The patient has a weakened immune system, making it harder to fight infections.
- The infection is causing trouble breathing, indicating a potential spread to critical areas.
While antibiotic treatment can help control bacterial growth, it is usually not a permanent solution. A root canal, tooth extraction, or deep cleaning may still be required to eliminate the infection completely.
How Long Before Antibiotics Relieve Tooth Pain?
The most pressing question for many patients is: how soon will antibiotics stop tooth pain?
Most antibiotics begin eliminating bacteria within 24 to 48 hours. However, pain relief varies based on factors such as the infection’s severity, the specific antibiotic prescribed, and the need for further dental treatment.
Here is a general timeline of what to expect:
- Mild infections – Pain may improve within 48 to 72 hours after starting antibiotic treatment.
- Moderate infections – Symptoms, including pain and swelling, may take 3 to 5 days to subside.
- Severe infections – Infections that have spread may require a full course of antibiotics (7 to 10 days) before significant relief is felt.
Even if symptoms subside, finishing the entire course of antibiotics is essential. Discontinuing treatment too early can contribute to antibiotic resistance, making future bacterial infections more difficult to manage.
Which Antibiotics Are Used for Tooth Infections?
The type of antibiotic treatment depends on the bacteria causing the dental infection. A dentist may recommend antibiotics such as:
- Amoxicillin – The most commonly prescribed antibiotic, taken every 8 to 12 hours.
- Clindamycin – Used for patients allergic to penicillin.
- Metronidazole – Sometimes combined with other antibiotics to enhance effectiveness.
- Azithromycin – A suitable option for patients with allergic reactions to other antibiotics.
A healthcare provider will select the most appropriate antibiotic treatment depending on the type of bacteria present.
Why Antibiotics Alone Won’t Fix a Tooth Infection
Many people assume that taking antibiotics will completely resolve a tooth infection, but this is not the case. Antibiotics work by controlling bacterial growth, but they do not remove the infected pulp inside the tooth.
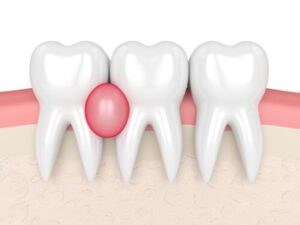 To fully treat infections, a dental professional may recommend:
To fully treat infections, a dental professional may recommend:
- Root canal treatment: Eliminates the infected pulp and seals the tooth to prevent future reinfection.
- Tooth extraction: Necessary if the tooth is beyond saving.
- Deep cleaning: Helps treat infections caused by gum disease.
The Australian Dental Association advises that antibiotics should not be used as a substitute for dental procedures, as they only offer temporary relief.
How to Support Antibiotic Treatment at Home
While waiting for antibiotics to work, you can use home remedies to ease discomfort:
- Warm salt water rinses: Helps reduce swelling and bacterial buildup.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Such as Ibuprofen or paracetamol, can help alleviate dental pain.
- Cold compress: Can be applied to the face to minimise swelling.
- Fluoride toothpaste: Strengthens teeth and prevents further tooth decay.
- Limiting sugary and acidic foods: Can prevent symptoms from worsening.
These methods may provide relief, but they do not replace professional dental treatment. If the pain does not go away, it is essential to see a dentist.
What If Your Tooth Infection Does Not Improve?
If symptoms do not improve after starting antibiotics, possible reasons include:
- The infection is severe and requires urgent dental work.
- The bacteria are resistant to the antibiotic prescribed.
- The patient is taking the wrong type of antibiotic.
- There is an undiagnosed dental abscess that requires additional treatment.
If pain, swelling, or trouble breathing worsens, it may indicate a serious infection that needs urgent medical attention.
How to Prevent Future Tooth Infections
Preventing tooth infections is easier than treating them. Practising good oral hygiene habits can significantly lower the risk of needing antibiotics for a tooth infection in the future.
Recommendations include:
- Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste.
- Flossing daily helps eliminate food debris and plaque, reducing the risk of infection.
- Routine dental visits for check-ups and professional cleanings help maintain oral health.
- Avoid smoking, which weakens the immune system.
- Seeking prompt dental treatment for cavities and tooth decay before they worsen.
By maintaining proper oral care, you can reduce the likelihood of developing dental infections and requiring antibiotic treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How soon will antibiotics stop tooth pain?
Most antibiotics for a tooth infection start working within 24 to 48 hours, but it can take 3 to 5 days for noticeable pain relief. However, the infection itself may not be completely gone until the full course of antibiotics is completed.
- Can I take antibiotics without seeing a dentist for a tooth infection?
No, antibiotics should only be taken when prescribed by a dentist or healthcare provider after assessing the severity of the infection. Self-medicating with antibiotics for a tooth infection can lead to improper treatment and contribute to antibiotic resistance.
- How do I know if my tooth infection is getting better with antibiotics?
If the antibiotics are working, you should notice a reduction in pain, swelling, and inflammation within 48 to 72 hours. However, if symptoms persist or worsen, you should contact your dental professional for further evaluation.
- What are the signs that my tooth infection is getting worse?
If you experience increasing pain, swelling, fever, trouble breathing, or difficulty swallowing, your infection may be spreading. A serious infection can become life-threatening, so seek immediate dental professional care if symptoms worsen.
- What should I do if I have an allergic reaction to antibiotics?
If you experience allergy symptoms such as rash, itching, swelling, difficulty breathing, or dizziness after taking antibiotics, seek immediate medical attention. Your healthcare provider may need to recommend a different antibiotic treatment.
- Can an infected tooth cause bad breath?
Yes, a tooth infection can result in ongoing bad breath caused by the accumulation of bacteria and pus. Practising good oral hygiene and receiving timely dental treatment can help resolve the issue.
- Can I take antibiotics on an empty stomach?
Some antibiotics work better when taken with food, while others should be taken on an empty stomach. Follow your dentist’s or healthcare provider’s instructions to ensure the antibiotic treatment is effective and to minimise stomach irritation.
- Can a tooth infection heal on its own without antibiotics or treatment?
No, a tooth infection will not go away on its own. Without proper dental treatment, the infection can extend and cause further complications. Seeking professional care is the only way to fully resolve the issue.
- What should I eat while taking antibiotics for a tooth infection?
 It is advised to eat soft, nutritious foods that will not aggravate the infection, such as:
It is advised to eat soft, nutritious foods that will not aggravate the infection, such as:
- Soups and broths
- Yoghurt and smoothies
- Mashed potatoes and scrambled eggs
- Cooked vegetables and soft fruits
Avoid hard, spicy, or acidic foods that may cause further discomfort.
- What should I do if antibiotics do not improve my symptoms?
If symptoms do not improve after starting antibiotics, you may need a different medication or additional dental treatment. Contact your dentist if you still experience pain, swelling, or infection symptoms after a few days of taking antibiotics.
Final Thoughts
So, how soon will antibiotics stop tooth pain? Most antibiotics begin to work within 24 to 48 hours, but full pain relief may take 3 to 5 days or longer, depending on the severity of the infection.
However, only antibiotics are not enough to cure a tooth infection. Proper dental treatment, such as a root canal, tooth extraction, or deep cleaning, is often necessary to eliminate the infection completely.
If you are experiencing dental pain, do not delay seeking professional care. A dental professional can determine the right course of action to prevent the infection from spreading and ensure long-term oral health.
Contact Definitive Dental today at (02) 6105 9833 to schedule an appointment and get the expert care you need for lasting relief.
Note: Any surgical or invasive procedure carries risks. Before proceeding, you should seek a second opinion from an appropriately qualified health practitioner.
References
- WebMD. (n.d.). Pulling a tooth (tooth extraction). Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/pulling-a-tooth-tooth-extraction
- Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Antibiotics for tooth infections. Retrieved from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/antibiotics-for-tooth-infections
- Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Tooth abscess: Symptoms & causes. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tooth-abscess/symptoms-causes/syc-20350901
- Healthline. (n.d.). How to make a cold compress. Retrieved from https://www.healthline.com/health/make-cold-compress



